jupyter notebook 가상환경에 basemap 설치하기
conda install -c anaconda basemap
설치 후 애러가 발생하지 않으면 괜찮은데 설치하는 도중 KeyError: 'PROJ_LIB'라는 애러가 자주 발생하는거 같다.
PROJ_LIB을 설정하기 위해
가상환경의 위치를 파악하자. conda env list를 입력

나의 경우 /root/anaconda3/envs/jupyter이다.
cd /root/anaconda3/envs/jupyter 입력 후 ls를 입력하면 share 가 존재하는 것을 확인 가능하다.

cd ./share 나 cd share로 경로 이동

proj가 존재하는 것을 확인했다.
os.environ["PROJ_LIB"] ='/root/anaconda3/envs/jupyter/share/proj'로 설정 후
from mpl_toolkits.basemap import Basemap, addcyclic, shiftgrid 를 실행하면 애러 없이 실행 되는 것을 확인 할 수 있다.

'python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [postgreSQL] python에서 postgreSQL과 shape file 사용하기 (0) | 2020.03.15 |
|---|---|
| python 메일 보내기 (0) | 2020.02.24 |
| numpy 정리(1) (0) | 2020.02.18 |
| 주피터 노트북 변수 보기 및 실행시간 자동확인(Extensions) (0) | 2020.02.16 |
| matplotlib 정리(1) (0) | 2020.02.16 |
QGIS와 postgreSQL 연동하기


이름 : QGIS에서 확인할 이름
호스트 : 도메인이나 외부 IP
포트 : 포트번호
데이터베이스 : postgreSQL DB명
확인 누르면 아래 창이 뜸

사용자 이름 : postgreSQL 사용자 이름
비밀번호 : 해당 비밀 번호
연결 버튼을 눌러주면 아래와 같이 나타남.

'GIS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Vworld WMS 등록하기 (0) | 2020.02.21 |
|---|
Vworld WMS 등록하기

http://api.vworld.kr/req/wfs?key=인증키&인증받은 은 도메인

WMS/WMTS>새 연결

http://api.vworld.kr/req/wms?key=인증키&domain=http://www.biz-gis.com&
플러그인> 플러그인 관리 및 설치>zip 파일에서 설치

https://plugins.qgis.org/plugins/tmsforkorea/
plugins.qgis.org

'GIS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| QGIS와 postgreSQL 연동하기 (0) | 2020.02.21 |
|---|
numpy 정리(1)
numpy 연습¶
1. dimension, type¶
- 부호가 있는 정수(i) : int(8, 16, 32, 64)
- 부호가 없는 정수(u) : unit(8, 16, 32, 64)
- 실수(f) : float(16, 32, 64, 128)
- 복소수(c) : complex(64, 128, 256)
- 불리언(b) : bool
- 문자열(S) : string
- 오브젝트(O) : object
- 유니코드(U) : unicode ### 2. sahpe, dtype, astype
- sahpe : 차원 확인
- dtype : 자료 형태 확인
- astype : 자료 형태 변환 ### 3. isinf, isnan
4. np.sign, np.ceil, np.floor¶
- sign : 양수는 1 음수는 -1 0은 0을 반환
- ceil : 올림
- floor : 버림 ### 5. np.multply(arr1,arr2), np.maximum(arr1,arr2)
- multply : 원소곱
- maximum : 원소 최대값 ### 6. min, mean, sum, std, argmin, argamx, cumsum, cumprod
- axis 옵션을 통해 행, 열, 전체에 적용 가능 ### 7. np.hstack(arr1(n,m1),arr2(n,m2)), np.vstack(arr1(n1,m),arr2(n2,m)) ### np.dstack(arr1(n,m),arr2(n,m)), np.stack(arr1(n,m),arr2(n,m))
- hstack : 행 병합 arr(n,m1+m2)
- vstack : 열 병합 arr(n1+n2,m)
- dstack : 원소 병합 arr(n,m,2)
- stack : axis=0(arr(2,n,m)), axis=1(arr(n,2,m)), axis=2(arr(n,m,2))
import numpy as np
data1 = [1,2,3,4,5]
data2 = [1,2,3,3.5,4]
arr1 = np.array(data1)
arr2 = np.array([1,2,3,4,5])
arr3 = np.array(data2)
arr4 = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9],[10,11,12]])
shape를 통해 차원을 확인 가능¶
arr1.shape
dtype을 통해 자료 형태 확인 가능
arr2.dtype
arr2 = np.array([1,2,3,4,5],dtype='b')
arr2
astype을 통해 자료 형태 변환 가능¶
arr2.astype('f')
inf과 nan 이 존재¶
- np.isinf(), np.isnan()으로 불리언화 할 수 있음
np.array([1])/np.array([0])
np.log(0)
np.array([0])/np.array([0])
- np.sign : 양수는 1 음수는 -1 0은 0 을 반환
- np.ceil : 올림
- np.floor : 버림
np.sign(arr1)
두 개의 array에 대해 동일한 위치의 성분끼리 연산 값을 계산하기(add, subtract, multiply, divide)¶
arr1
np.random.seed(1)
arr1=np.ceil(np.random.randn(5,3)*10)
print(arr1)
np.random.seed(2)
arr2=np.ceil(np.random.randn(5,3)*10)
print(arr2)
np.abs(arr1)
np.sqrt(arr1)
np.square(arr1)
np.exp(arr1)
np.log(arr1)
print(arr1)
print(arr2)
np.multiply(arr1,arr2)
np.maximum(arr1,arr2)
min, mean, sum, std, argmin, argamx, cumsum,cumprod
arr1
np.min(arr1,axis=0)
np.mean(arr1, axis=0)
np.mean(arr1)
np.argmin(arr1,axis=0)
np.argmin(arr1,axis=1)
np.cumprod(arr1,axis=0)
arr1
np.sort(arr1,axis=0)
np.sort(arr1,axis=0)[::-1]
a = np.arange(12)
a
b = a.reshape(3, 4)
b
a.reshape(6, -1)
a.reshape(2, -1, 3)
a.reshape(2,-1,3).flatten()
a.reshape(12,1)
a[np.newaxis]
a[:,np.newaxis]
a.reshape(3,-1)
np.array(range(9)).reshape(3,-1)
b=np.hstack((a.reshape(3,-1),np.array(range(9)).reshape(3,-1)))
b
b.shape
a.reshape(4,-1)
np.array(range(9)).reshape(3,-1)
np.vstack((a.reshape(4,-1),np.array(range(9)).reshape(3,-1)))
arr1
arr2
np.dstack((arr1,arr2))
np.dstack((arr1,arr2)).shape
np.stack((arr1,arr2))
np.stack((arr1,arr2)).shape
np.stack((arr1,arr2),axis=1)
np.stack((arr1,arr2),axis=1).shape
np.stack((arr1,arr2),axis=2)
x = np.arange(3)
y = np.arange(5)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
X
Y
[list(zip(x, y)) for x, y in zip(X, Y)]
'python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| python 메일 보내기 (0) | 2020.02.24 |
|---|---|
| jupyter notebook 가상환경에 basemap 설치하기 (0) | 2020.02.23 |
| 주피터 노트북 변수 보기 및 실행시간 자동확인(Extensions) (0) | 2020.02.16 |
| matplotlib 정리(1) (0) | 2020.02.16 |
| 주피터 노트북에 메모리 사용량 모니터링 하기 (0) | 2020.01.24 |
주피터 노트북 변수 보기 및 실행시간 자동확인(Extensions)
conda install -c conda-forge jupyter_contrib_nbextensions
!jupyter contrib nbextension install --user
!jupyter nbextension enable codefolding/main
!pip install jupyter_contrib_nbextensions && jupyter contrib nbextension install
conda install -c conda-forge yapf위를 통해서 NBEXTENSIONS를 설치하자.
망치모양 왼쪽에 표적모양이 변수리스트를 출력해주는 형태
위와 같이 뜬다면 성공 아니면 아래와 같은 과정으로 설정
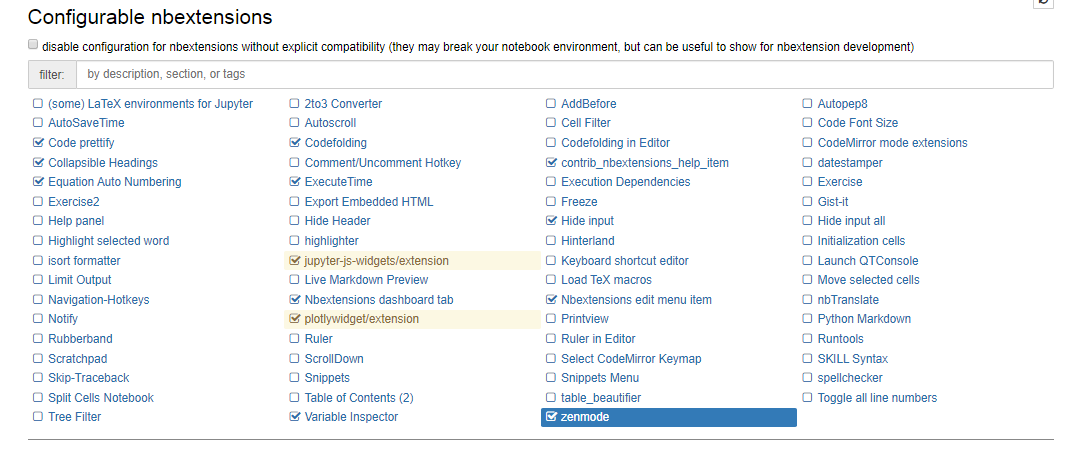
'python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| jupyter notebook 가상환경에 basemap 설치하기 (0) | 2020.02.23 |
|---|---|
| numpy 정리(1) (0) | 2020.02.18 |
| matplotlib 정리(1) (0) | 2020.02.16 |
| 주피터 노트북에 메모리 사용량 모니터링 하기 (0) | 2020.01.24 |
| python 회귀분석 할 때 주로 사용할 것 같은 패키지 및 코드 (0) | 2020.01.14 |
matplotlib 정리(1)
#한글 폰트 안깨지게 설정
import platform
from matplotlib import font_manager, rc
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
if platform.system() == 'Windows':
path = "c:/Windows/Fonts/malgun.ttf"
font_name = font_manager.FontProperties(fname=path).get_name()
rc('font', family=font_name)
elif platform.system() == 'Darwin':
rc('font', family='AppleGothic')
elif platform.system() == 'Linux':
rc('font', family='NanumBarunGothic')
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
x = np.arange(1,10)
y = x*5
plt.plot(x,y)
plt.show()
선 색깔 바꾸기
#b, g, r, c, m, y, b, w
plt.plot(x,y,'m')
x = np.arange(1,10)
y = x*5
plt.plot(x,y,'.')
마커 종류¶
. : point\ , : pixel\ o : circle\ v : triangle_down\ ^ : traingle_up\ < : traingle_left\ > : traingle_right\ 1 : tri_down\ 2 : tri_up\ 3 : tri_left\ 4 : tri_right\ s : square\ p : pentagon\ * : star\ h : hexagon1\ H : hexagon2\ + : plus\ x : x\ D : diamond\ d : thin_diamond\
plt.plot(x,y,'x')
선 종류¶
- solid\ -- dashed\ -. dash-dot\ \: dotted
plt.plot(x,y,':')
color(c) : 선색깔\ linewidth(lw) : 선굵기\ linestyle(ls) : 선스타일\ marker : 마커의 종류\ markersize(ms) : 마커의 크기\ markeredgecolor(mec) : 마커 선 색깔\ markeredgewidth(mew) : 마커 선 굵기\ markerfacecolor(mfc) : 마커 내부 색깔
plt.plot([10, 20, 30, 40], [1, 4, 9, 16], c="b",
lw=5, ls="--", marker="o", ms=15, mec="g", mew=5, mfc="r")
plt.plot([10, 20, 30, 40], [1, 4, 9, 16], c="b",
lw=5, ls="--", marker="o", ms=15, mec="g", mew=5, mfc="r")
plt.title("스타일 적용 예")
plt.show()
틱 : 플롯이나 차트에서 축의 위치 표시 지점 plt.xticks(표시 간격, 표시 형태)\ ex)\ plt.xticks([-np.pi, -np.pi / 2, 0, np.pi / 2, np.pi], [r'$-\pi$', r'$-\pi/2$', r'$0$', r'$+\pi/2$', r'$+\pi$'])\ plt.yticks([-1, 0, 1], ["Low", "Zero", "High"])
plt.plot(x,y)
plt.xticks(range(2,10,3))
plt.yticks(range(0,50,10))
plt.show()
X = np.linspace(-np.pi, np.pi, 256)
C = np.cos(X)
plt.title("x축과 y축의 tick label 설정")
plt.plot(X, C)
plt.xticks([-np.pi, -np.pi / 2, 0, np.pi / 2, np.pi])
plt.yticks([-1, 0, +1])
plt.show()
t = np.arange(0., 5., 0.2)
plt.title("라인 플롯에서 여러개의 선 그리기")
plt.plot(t, t, 'r--',
t, 0.5 * t**2, 'bs:',
t, 0.2 * t**3, 'g^-')
plt.show()
plt.title("복수의 plot 명령을 한 그림에서 표현")
plt.plot([1, 4, 9, 16],
c="b", lw=5, ls="--", marker="o", ms=15, mec="g", mew=5, mfc="r")
# plt.hold(True) # <- 1,5 버전에서는 이 코드가 필요하다.
plt.plot([9, 16, 4, 1],
c="k", lw=3, ls=":", marker="s", ms=10, mec="m", mew=5, mfc="c")
# plt.hold(False) # <- 1,5 버전에서는 이 코드가 필요하다.
plt.show()
범례(legend)¶
best : 0\ upper right : 1\ upper left : 2\ lower left : 3\ lower right : 4\ right : 5\ center left : 6\ center right : 7\ lower center : 8\ upper center : 9\ center : 10
X = np.linspace(-np.pi, np.pi, 256)
C, S = np.cos(X), np.sin(X)
plt.title("legend를 표시한 플롯")
plt.plot(X, C, ls="--", label="cosine")
plt.plot(X, S, ls=":", label="sine")
plt.legend(loc=0)
plt.show()
라벨(label)¶
xlabel, ylabel, title
X = np.linspace(-np.pi, np.pi, 256)
C, S = np.cos(X), np.sin(X)
plt.plot(X, C, label="cosine")
plt.xlabel("time")
plt.ylabel("amplitude")
plt.title("Cosine Plot")
plt.show()
그림의 구조¶
Figure 객체(그림이 그려지는 캔버스), Axes객체(하나의 플롯), Axis 객체(하나의 축) 등으로 구성 plt.subplot(행,열,위치)를 통해 한 Figure내에 여러 Axes 를 표현 가능\ plt.gcf()를 통해 Figure 객체를 얻을 수 있음. plt.gca()를 통해 Axes 객체를 얻을 수 있음.
f1 = plt.figure(1)
plt.title("현재의 Figure 객체")
plt.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], 'ro:')
f2 = plt.gcf()
print(f1, id(f1))
print(f2, id(f2))
plt.show()
x1 = np.linspace(0.0, 5.0)
x2 = np.linspace(0.0, 2.0)
y1 = np.cos(2 * np.pi * x1) * np.exp(-x1)
y2 = np.cos(2 * np.pi * x2)
ax1 = plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(x1, y1, 'yo-')
plt.title('A tale of 2 subplots')
plt.ylabel('Damped oscillation')
print(ax1)
ax2 = plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(x2, y2, 'r.-')
plt.xlabel('time (s)')
plt.ylabel('Undamped')
print(ax2)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
plt.subplot(221)
plt.plot(np.random.rand(5))
plt.title("axes 1")
plt.subplot(222)
plt.plot(np.random.rand(5))
plt.title("axes 2")
plt.subplot(223)
plt.plot(np.random.rand(5))
plt.title("axes 3")
plt.subplot(224)
plt.plot(np.random.rand(5))
plt.title("axes 4")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Axis 객체와 축¶
twinx 명령어를 통해 복수의 y축을 가진 플롯을 표기 가능
fig, ax0 = plt.subplots()
ax1 = ax0.twinx()
ax0.set_title("2개의 y축 한 figure에서 사용하기")
ax0.plot([10, 5, 2, 9, 7], 'r-', label="y0")
ax0.set_ylabel("y0")
ax0.grid(False)
ax1.plot([100, 200, 220, 180, 120], 'g:', label="y1")
ax1.set_ylabel("y1")
ax1.grid(False)
ax0.set_xlabel("공유되는 x축")
plt.show()
plt.savefig('./임시.png')
plt.grid()
범위(range)¶
plt.xlim(최소,최대) plt.ylim(최소,최대)
linspace(x1,x2,n) : (x2-x1)/(n-1) 간격의 점 n 개 생성
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.4)
t = np.arange(0.01, 20.0, 0.01)
# log y axis
plt.subplot(221)
plt.semilogy(t, np.exp(-t/5.0))
plt.title('semilogy')
plt.grid(True)
# log x axis
plt.subplot(222)
plt.semilogx(t, np.sin(2*np.pi*t))
plt.title('semilogx')
plt.grid(True)
# log x and y axis
plt.subplot(223)
plt.loglog(t, 20*np.exp(-t/10.0), basex=2)
plt.grid(True)
plt.title('loglog base 2 on x')
# with errorbars: clip non-positive values
ax = plt.subplot(224)
ax.set_xscale("log", nonposx='clip')
ax.set_yscale("log", nonposy='clip')
x = 10.0**np.linspace(0.0, 2.0, 20)
y = x**2.0
plt.errorbar(x, y, xerr=0.1*x, yerr=5.0 + 0.75*y)
ax.set_ylim(ymin=0.1)
ax.set_title('Errorbars go negative')
plt.show()
X = np.linspace(-np.pi, np.pi, 256,endpoint=True)
C,S = np.cos(X), np.sin(X)
plt.figure(figsize=(10,6), dpi=80)
plt.plot(X, C, color="blue", linewidth=2.5, linestyle="-", label="cosine")
plt.plot(X, S, color="red", linewidth=2.5, linestyle="-", label="sine")
# Set limits
plt.xlim(X.min()*1.1, X.max()*1.1)
plt.ylim(C.min()*1.1, C.max()*1.1)
# Setting tick labels
plt.xticks([-np.pi, -np.pi/2, 0, np.pi/2, np.pi], [r'$-\pi$', r'$-\pi/2$', r'$0$', r'$+\pi/2$', r'$+\pi$'])
plt.yticks([-1, 0, +1], [r'$-1$', r'$0$', r'$+1$'])
# # Moving spines
ax = plt.gca()
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('bottom')
ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(('data',0))
ax.yaxis.set_ticks_position('left')
ax.spines['left'].set_position(('data',0))
# Adding a legend
plt.legend(loc='upper left', frameon=False)
ax
t = 2*np.pi/3
plt.plot([t,t],[0,np.cos(t)], color ='blue', linewidth=1.5, linestyle="--")
plt.scatter([t,],[np.cos(t),], 50, color ='blue')
plt.annotate(r'$\sin(\frac{2\pi}{3})=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$',
xy=(t, np.sin(t)), xycoords='data',
xytext=(+10, +30), textcoords='offset points', fontsize=16,
arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->", connectionstyle="arc3,rad=.2"))
plt.plot([t,t],[0,np.sin(t)], color ='red', linewidth=1.5, linestyle="--")
plt.scatter([t,],[np.sin(t),], 50, color ='red')
plt.annotate(r'$\cos(\frac{2\pi}{3})=-\frac{1}{2}$',
xy=(t, np.cos(t)), xycoords='data',
xytext=(-90, -50), textcoords='offset points', fontsize=16,
arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->", connectionstyle="arc3,rad=.2"))
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
fig = plt.figure()
ax = Axes3D(fig)
X = np.arange(-4, 4, 0.25)
Y = np.arange(-4, 4, 0.25)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y)
R = np.sqrt(X**2 + Y**2)
Z = np.sin(R)
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap='hot')
plt.show()
'python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| numpy 정리(1) (0) | 2020.02.18 |
|---|---|
| 주피터 노트북 변수 보기 및 실행시간 자동확인(Extensions) (0) | 2020.02.16 |
| 주피터 노트북에 메모리 사용량 모니터링 하기 (0) | 2020.01.24 |
| python 회귀분석 할 때 주로 사용할 것 같은 패키지 및 코드 (0) | 2020.01.14 |
| power shell 을 활용하여 windows에 jupyter notebook 설치하기 (0) | 2019.06.27 |
